

 verb conjugations and common mistakes." width="500" height="500" />
verb conjugations and common mistakes." width="500" height="500" />
The spelling of he/she/it is different in the present simple. Check how it changes below. The spelling is the same for all the other persons.
We often use the present simple with adverbs of frequency (always, sometimes, etc.) and expressions of frequency (once every three months, twice a week, every other day, etc.).
Adverbs of frequency go in mid position (before the main verb or after be).
Expressions of frequency go at the end of the sentence
 the form of the Present Continuous tense in positive, negative, and question forms, including short answers and spelling rules for -ing words." width="500" height="500" />
the form of the Present Continuous tense in positive, negative, and question forms, including short answers and spelling rules for -ing words." width="500" height="500" />
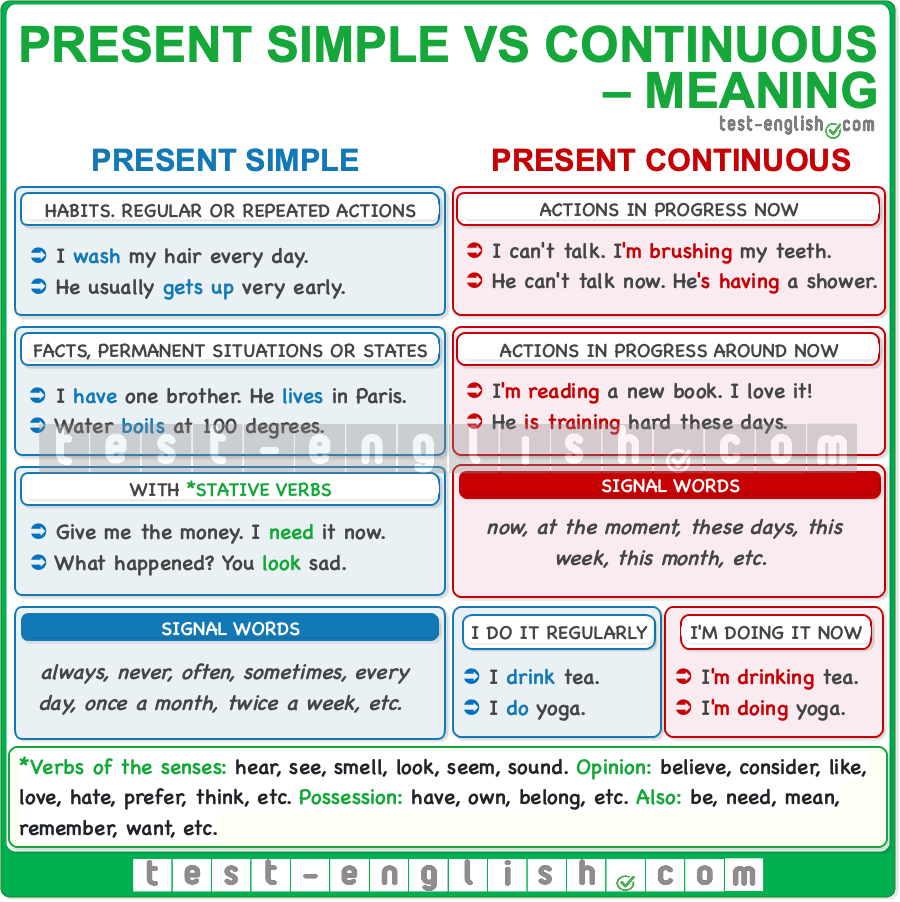
We use the present continuous to talk about things that are happening now or ‘around now’ (a time around this moment, such as these days, weeks or months)
The present continuous is used for temporary actions:
The present continuous often appears next to expressions such as now, these days, this week/month, or at the moment.
Non–action verbs (or stative verbs) cannot be used in the present continuous. They must be used in the present simple. The most frequent are the verbs of the senses (hear, see, smell, etc. ), verbs of opinion (believe, consider, like, love, hate, prefer, think, etc.), and other verbs like be, have, need, want, etc.
 with signal words and examples of each." width="500" height="500" />
with signal words and examples of each." width="500" height="500" />
We're developing a NEW LEARNING PLATFORM with a subscription plan that includes additional features at an affordable price. One of those features will be PDF downloads. Learn more!